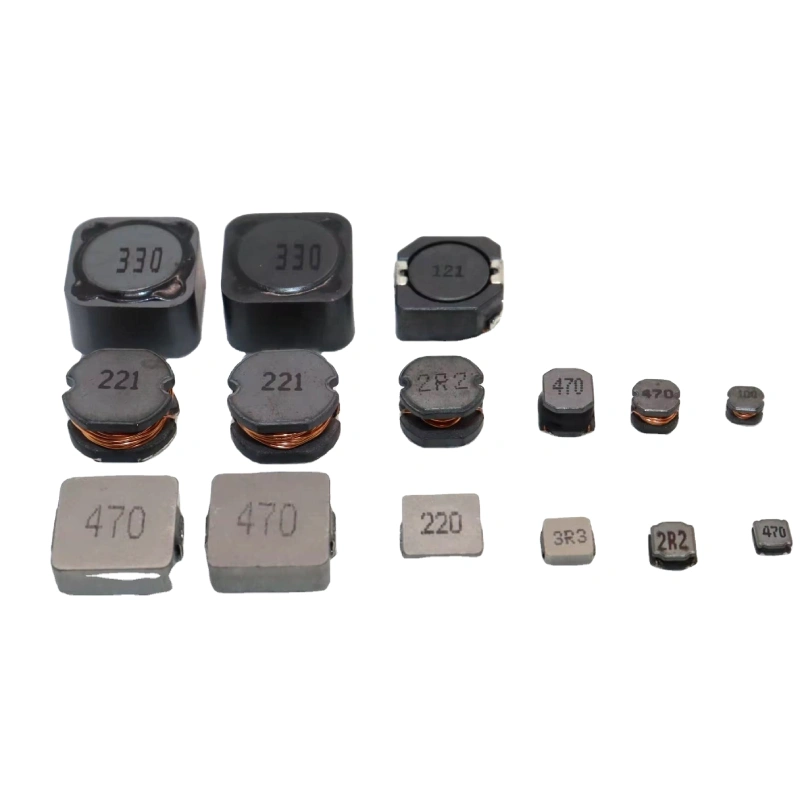
The most common common mode inductor in daily life is computer applications. The motherboard inside the computer is mixed with various high-frequency circuits, digital circuits and analog circuits. When they work, they will generate a large amount of high-frequency electromagnetic waves that interfere with each other. This is EMI. Common mode inductors and differential mode inductors are two electronic components that are particularly commonly used. For most electronic products, they are very important electronic components. People often compare common mode inductors and differential mode inductors. So today we will briefly introduce the differences between common mode inductors and differential mode inductors
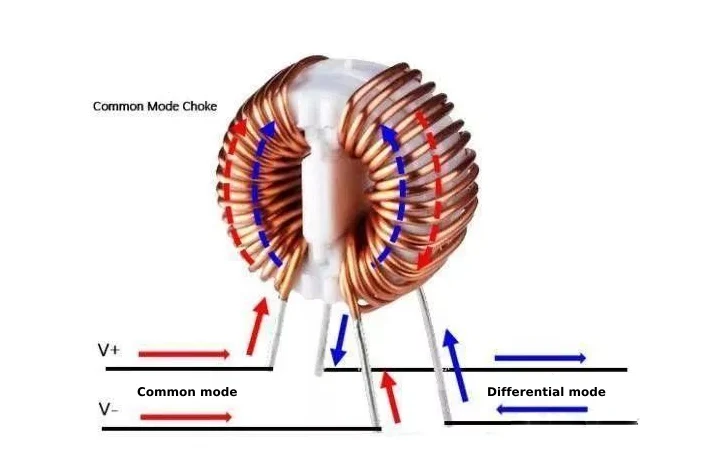
Common mode inductors and differential mode inductors are both effective components for resisting electromagnetic interference and are widely used in various filters, switching power supplies and other products. However, common-mode inductors are used to suppress common-mode interference, while differential-mode inductors are used to suppress differential-mode interference. Both are relatively important filter inductors.
Common mode inductors are common-mode interference suppression devices with ferrite as the core. They are composed of two coils of the same size and number of turns symmetrically wound on the same ferrite magnetic ring core to form a four-terminal device. It has a large inductance and can suppress common mode signals, but the leakage inductance is very small and has almost no effect on differential-mode signals.
The principle is that when the common-mode current flows through, the magnetic flux in the magnetic ring is superimposed on each other, so it has a considerable inductance, thereby suppressing the common-mode current. When the differential-mode current flows through the two coils, the magnetic flux in the magnetic ring cancels each other, and there is almost no inductance, and the differential-mode current can pass without attenuation.
Therefore, common-mode inductors can effectively suppress common-mode interference signals in balanced lines without affecting the differential-mode signals normally transmitted on the lines.
(★ If you want to know more information, you can refer to the following article: •What Are The Functions Of Common Mode Inductors In Circuits?)

Differential mode inductance is a characteristic of a closed loop, that is, when the current through the closed loop changes, an electromotive force will appear to resist the change in current. This inductance is called self-inductance and is a characteristic of the closed loop itself. Assuming that the current in one closed loop changes, an electromotive force will also be generated in the other closed loop due to induction. This inductance is called mutual inductance. Inductors are circuit components specifically used to implement inductance in circuits. A solenoid is a simple inductor, which refers to a multi-wound wire (called a “coil”), which can be hollow or have a metal core inside.
The inductance of a solenoid is self-inductance. A transformer is an inductor composed of two coupled coils. Because it has mutual inductance characteristics, it is a basic magnetic circuit component.
Although both inductors are filter inductors, their different functions determine that their appearance and winding methods will also be different. For common-mode inductors, they are wound on the same iron core, and the wire diameter and number of turns of the two sets of windings are the same, but the winding directions are opposite. A set of coils has two pins, so the common-mode inductor will have 4 pins.
The differential-mode inductor is wound on the iron core, with only one coil, so there are only 2 pins. Therefore, the number of pins can be used to distinguish between common-mode inductors and differential-mode inductors.
The difference between common-mode inductors and differential-mode inductors
1. There are two types of inductors used to resist electromagnetic wave interference: common-mode inductors and differential-mode inductors.
2. The disturbance electromagnetic field generates differential-mode current between the line and the line, causing interference to the load, which is differential-mode interference. The disturbance electromagnetic field generates common-mode current between the line and the ground, and the common-mode current generates differential-mode voltage on the load, causing interference, which is common-mode ground loop interference.
3. The filter inductor that suppresses common-mode interference is called common-mode inductor. The filter inductor that suppresses differential-mode interference is called differential-mode inductor.
4. Common-mode inductors are two sets of coils with equal turns, equal wire diameters, and opposite winding directions wound on the same magnetic core. Differential-mode inductors are coils wound on an iron core.
5. The characteristics of common-mode inductors are: since the two sets of coils on the same iron core are wound in opposite directions, the iron core is not afraid of saturation, and the most commonly used magnetic core material on the market is high-conductivity ferrite material.
The characteristics of differential mode inductors are: they are used in high current situations. Since the coil is wound on an iron core, when the current flowing into the coil increases, the iron core in the coil will be saturated, so the most commonly used iron core material on the market is metal powder core material. Especially iron powder core material (due to its low price)
When the AC frequency is constant, the greater the inductance, the greater the resistance to AC, and the smaller the inductance, the smaller the resistance. Secondly, when the inductance is constant, the higher the AC frequency, the greater the resistance of the inductor to AC, and the lower the frequency, the smaller the resistance of the inductor to AC. In other words, the inductor has the characteristics of not allowing AC to pass through and allowing DC to pass through.
The ideal inductor is a pure inductor. It has no capacitance to allow AC to pass through, no resistance to allow DC to pass through, and no loss, so no matter how large its inductance is, it can completely prevent AC from passing through.
Generally speaking, common-mode inductors and differential-mode inductors differ in production processes, functions in circuits, electrical performance characteristics, etc. These differences also adapt to the needs of products in different industries for inductors, so there is no need to pay too much attention to their advantages and disadvantages, but to see whether they are more suitable in the current application!







